What is biological diversity?
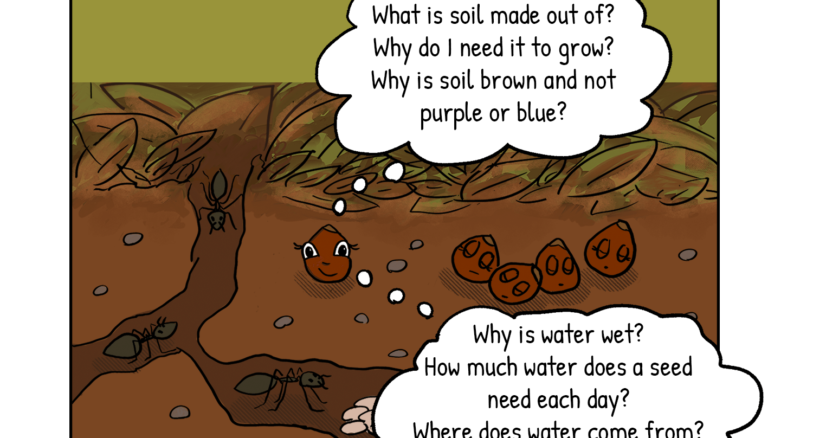
Biological diversity is the variety of all the living things on Earth. That incudes plants, fungi, animals, and microorganisms. It also includes the genes that code for life. Biological diversity is called biodiversity for short.
We can think about the variety of life in different ways. We can look at the total biodiversity of Earth – all life on our planet. We can look at the biodiversity in our own backyard. We can look at the biodiversity contained in a teaspoon of soil. We can also think of genetic differences between or within species.
We can look at the diversity of ecosystems. There are different types of ecosystems that have different environmental conditions. For example, rainforest, desert, grassland, wetland, and coral reef are all types of ecosystems.
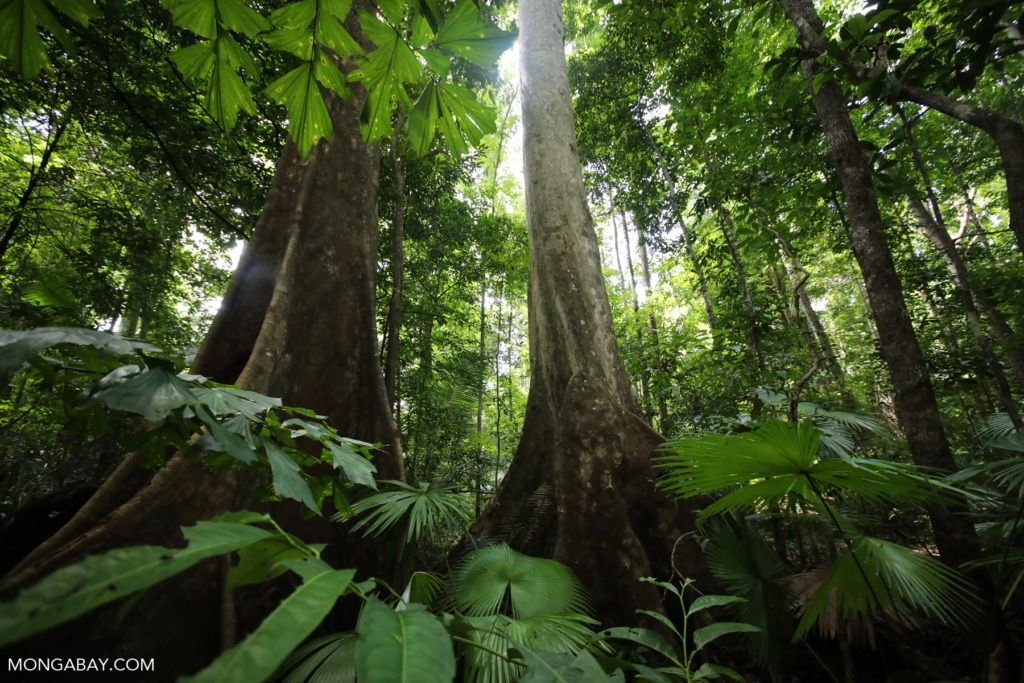
Some types of ecosystems support a greater number of species than others. Tropical rainforests have high species diversity. (Learn why rainforests have so many kinds of plants and animals.) Deserts have lower species diversity than tropical rainforests.
Although rainforests are home to more species, desert species are not less important than rainforest species. All species have a role to play in the ecosystem in which they live.
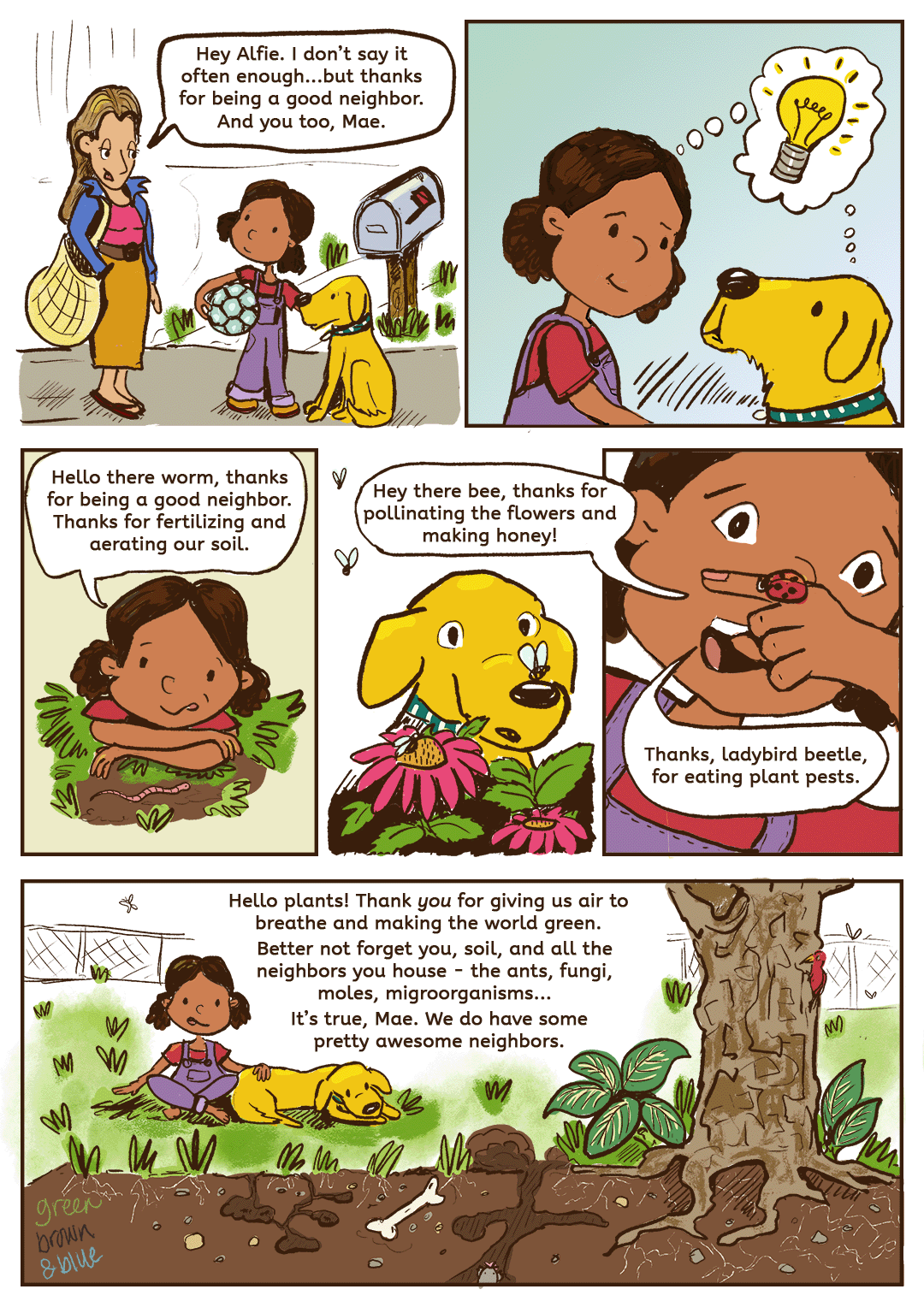
Biodiversity is beautiful and fascinating. We rely on biodiversity for things we need, such as clean water, air to breathe, shelter, food, and medicine.
May 22 is the International Day for Biological Diversity
The theme for this year (2023) is building back biodiversity. You can start in your own backyard or local park. Observe and appreciate the many species that are your neighbors.
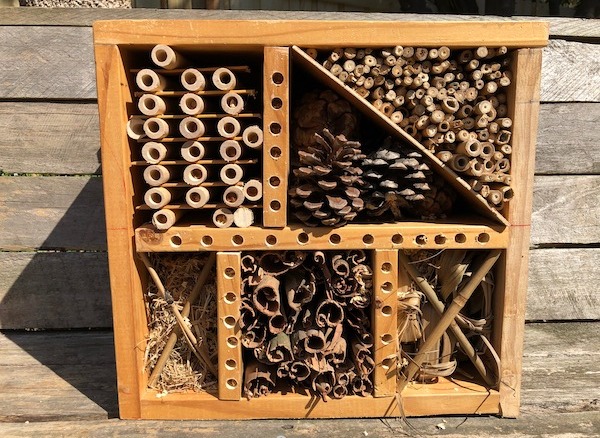
There are many ways to nurture biodiversity at home. You can grow native plants. You can build habitat for your local insects. You can take care of the soil.
For more information, visit the UN Environment Program website.
You may like these stories
Lesson: What is biodiversity and why is it important?



We need bees. How can you help?